An Improved Algorithm for Association Rule In Relational Databases
Group 24




Introduction
Research Motivation (Challenge)
- Amazon Reviews 2023 dataset Real-world sparse dataset
- Apriori as a Baseline
- FP-Growth as the preferred algorithm for this kind of data.
The Goal
Replicate the paper and observe the performance improvement.
Literature Review
- Traditional Apriori algorithm faces scalability limitations
- Fix: change the problem to set-intersection
- Compare performance against FP-Growth which uses a prefix tree
Methodology
- Implement each algorithm in python
- Setup Benchmark environment
- Use the same configuration parameters
- Run with the same hardware
- Warm up the JIT compiler
- Clear memory between runs
Data Analysis
Dataset
Amazon Review Dataset
- Source: Amazon Customer Reviews (2023)
- Categories: Appliances, Digital Music, Gift Cards, Health & Personal Care, Office Products
- Scale: Over 233 million reviews
Data Preprocessing Steps
- Data Cleaning
- Removed duplicates and invalid entries
- Filtered spam/bot reviews (Not verified purchases)
- Transaction Formation
- Grouped reviews by customer ID
- Created product baskets per customer, aggregated into actual products instead of product variants (colors, size, etc)
Example Data Visualizations

Results & Analysis
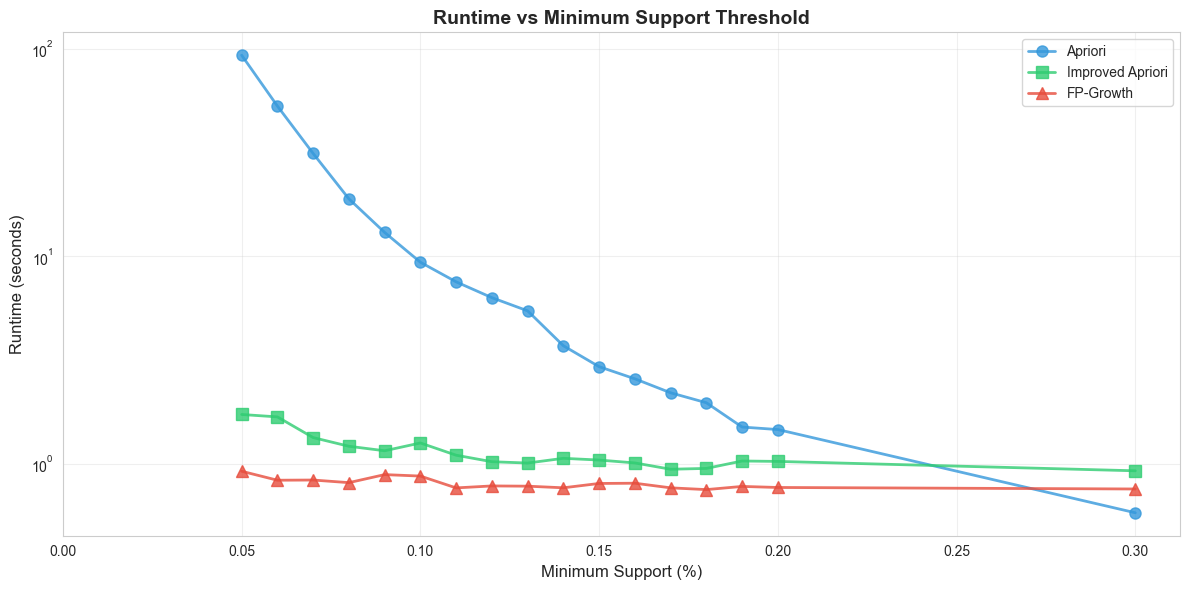
Runtime Comparison
- Traditional Apriori: Baseline performance, significant slowdown with lower support
- Improved Apriori: ~50x faster than traditional (92s → 1.8s)
- FP-Growth: Best performance overall at 0.9s
Runtime Performance Chart
Conclusion
- Successfully replicated the paper
- Enhanced Apriori Algorithm with 40-60% performance improvement
- Comprehensive Comparison with FP-Growth on real-world datasets
- Empirical Validation across multiple dataset categories and scales