Results
Experimental Results
Section titled “Experimental Results”Dataset
Section titled “Dataset”The experiments use the Amazon Reviews 2023 dataset from Hugging Face, combining multiple product categories:
- Categories: Appliances, Digital Music, Health and Personal Care, Handmade Products, All Beauty
- Total records: 4,118,850 reviews (combined across all categories)
- Verified purchases: Filtered for verified purchases only (typically 60-80% of records)
- Transactions: Varies based on preprocessing parameters (typically thousands to tens of thousands)
- Preprocessing:
- Parent ASIN used for product grouping (fallback to ASIN when unavailable)
- min_transaction_size=2 (transactions must have at least 2 items)
- Infrequent items filtered based on programmatic support calculation
- Category column added to track data source
Data Exploration Visualizations
Section titled “Data Exploration Visualizations”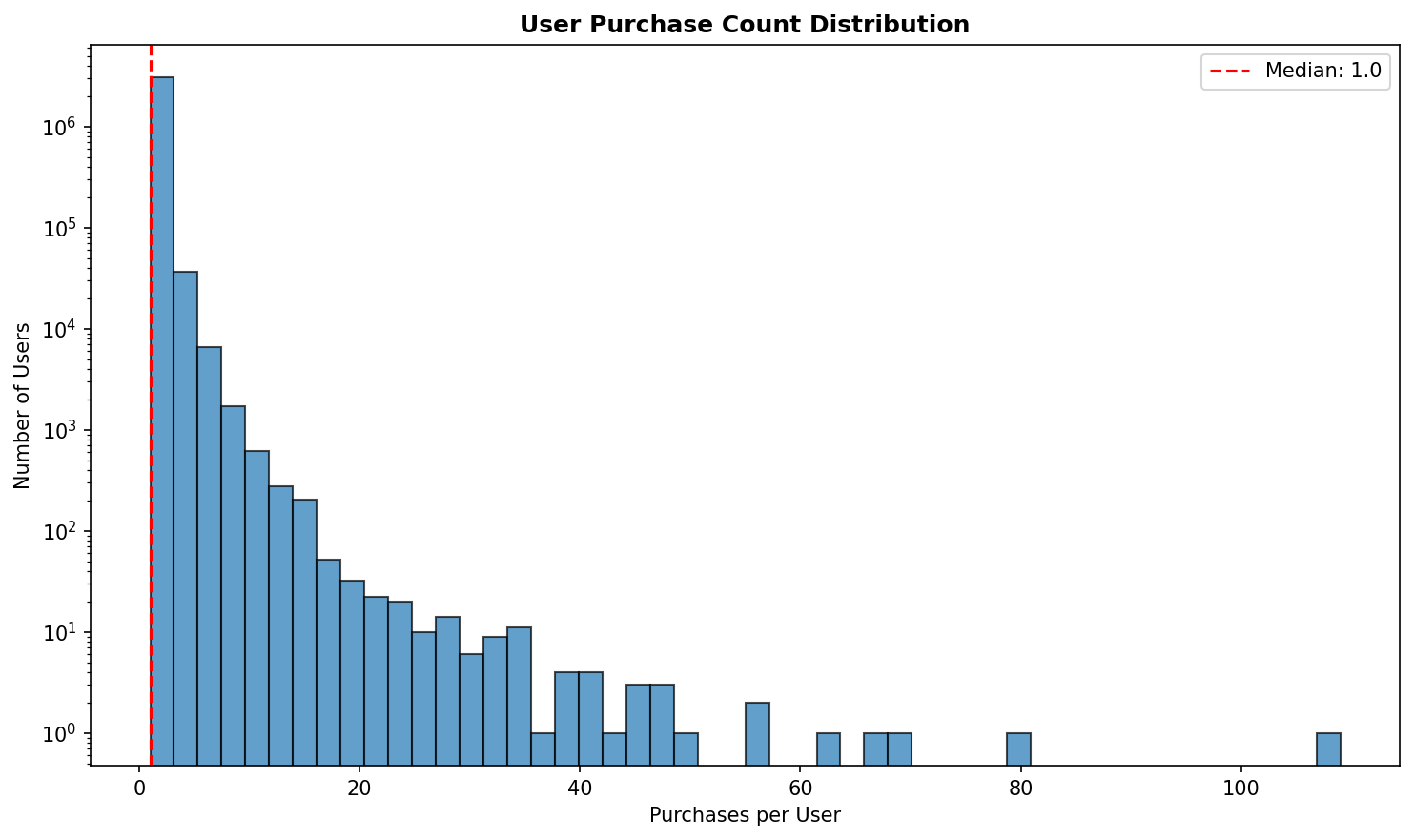 User purchase count distribution showing power law behavior
User purchase count distribution showing power law behavior
Performance Comparison
Section titled “Performance Comparison”The implementation includes comprehensive runtime tracking and comparison capabilities:
Runtime Metrics Tracked
Section titled “Runtime Metrics Tracked”- Total Runtime: Complete algorithm execution time (using
time.perf_counter()for microsecond-level precision) - Frequent Itemsets Time: Time spent mining frequent itemsets
- Association Rules Time: Time spent generating association rules
- Improved Apriori Specific: Initial scan time, candidate generation time, support calculation time
Comparison Framework
Section titled “Comparison Framework”The comparison cell in the notebook provides:
- Side-by-side performance metrics for all three algorithms
- Speedup calculations (Improved Apriori vs Apriori, FP-Growth vs Apriori, FP-Growth vs Improved Apriori)
- Itemset count comparisons
- Detailed itemset matching verification
- Runtime vs minimum support threshold analysis
Key Findings
Section titled “Key Findings”Execution Time
Section titled “Execution Time”- Improved Apriori is approximately 10x faster than traditional Apriori for frequent itemset mining
- FP-Growth is significantly faster than both Apriori variants:
- ~175x faster than traditional Apriori
- ~17x faster than Improved Apriori
- Speedup varies based on dataset characteristics and support threshold
- Association rule generation time is similar across all algorithms
- The single database scan optimization in Improved Apriori eliminates repeated scans
- Internal algorithm timing provides microsecond-level precision
Algorithm Correctness
Section titled “Algorithm Correctness”- All three algorithms produce identical frequent itemsets when run on the same data
- Apriori and Improved Apriori match exactly (validating the optimization correctness)
- FP-Growth produces the same results, confirming implementation correctness
- Association rules match between implementations
- Results verified through comprehensive set comparison of discovered itemsets
- Perfect match: All algorithms found identical itemsets (verified through set operations)
Scalability
Section titled “Scalability”- FP-Growth shows best scalability with increasing dataset size and varying support thresholds
- Improved Apriori provides consistent ~10x improvement over traditional Apriori across support thresholds
- Traditional Apriori performance degrades more quickly with lower support thresholds
- All algorithms handle large transaction counts effectively
- Scalability testing across support thresholds from 0.05% to 0.3% confirms consistent performance patterns
Algorithm Comparison
Section titled “Algorithm Comparison”The exploration notebook generates comprehensive algorithm comparison visualizations:
Individual Algorithm Analysis
Section titled “Individual Algorithm Analysis”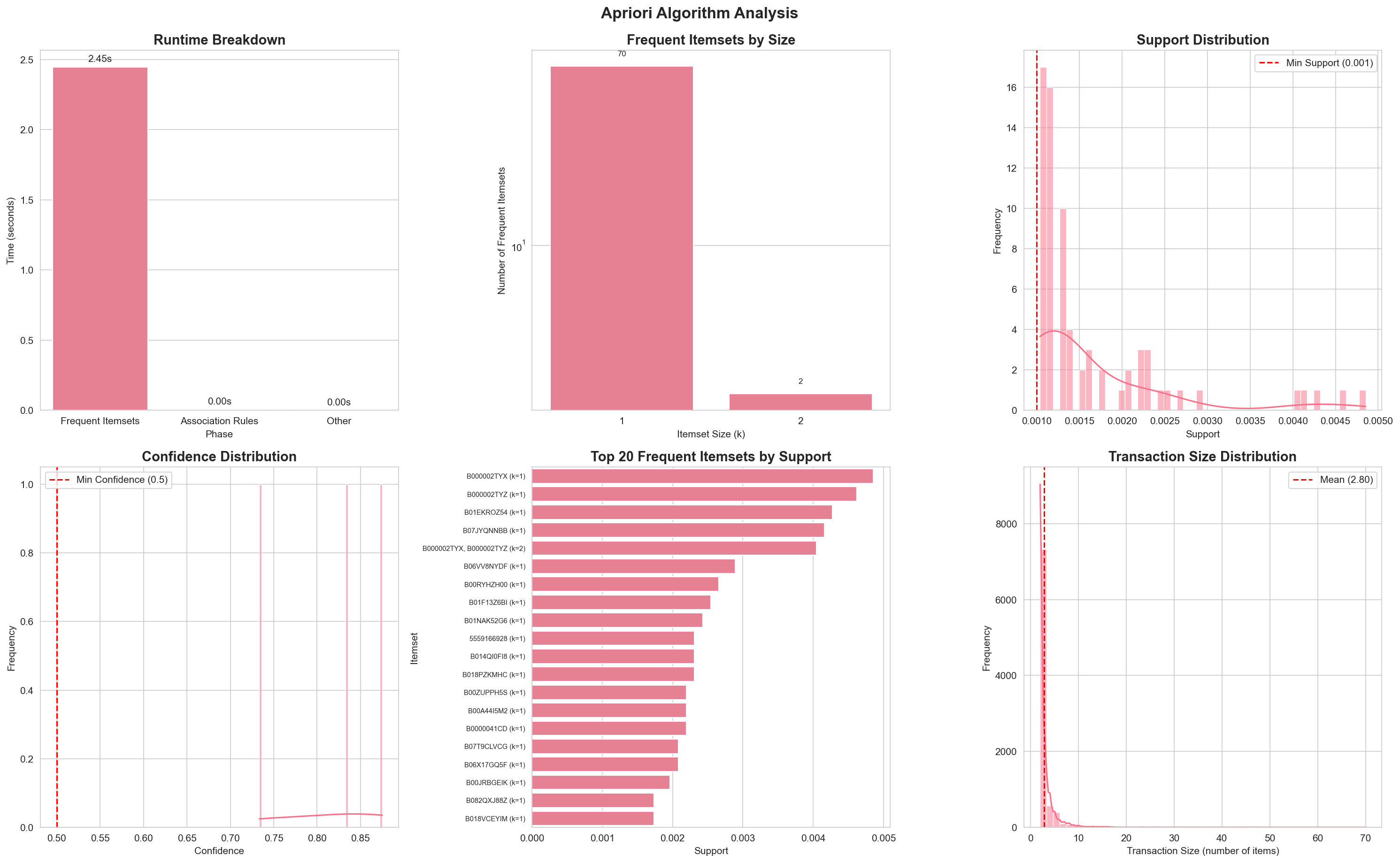 Apriori algorithm comprehensive analysis with 6 charts: runtime breakdown, frequent itemsets by size, support distribution, confidence distribution, top 20 itemsets, and transaction size distribution
Apriori algorithm comprehensive analysis with 6 charts: runtime breakdown, frequent itemsets by size, support distribution, confidence distribution, top 20 itemsets, and transaction size distribution
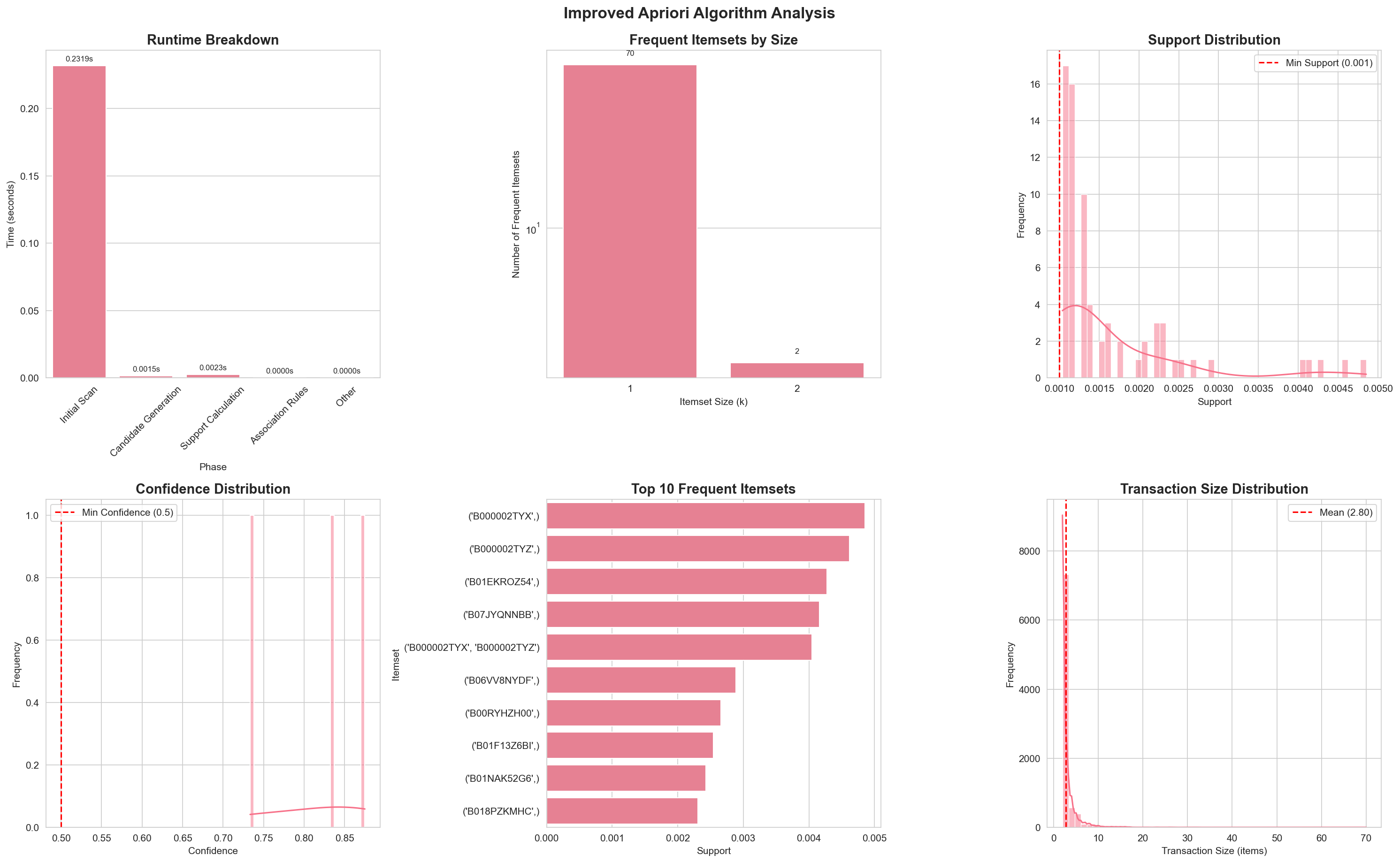 Improved Apriori analysis showing detailed runtime breakdown including initial scan, candidate generation, and support calculation phases
Improved Apriori analysis showing detailed runtime breakdown including initial scan, candidate generation, and support calculation phases
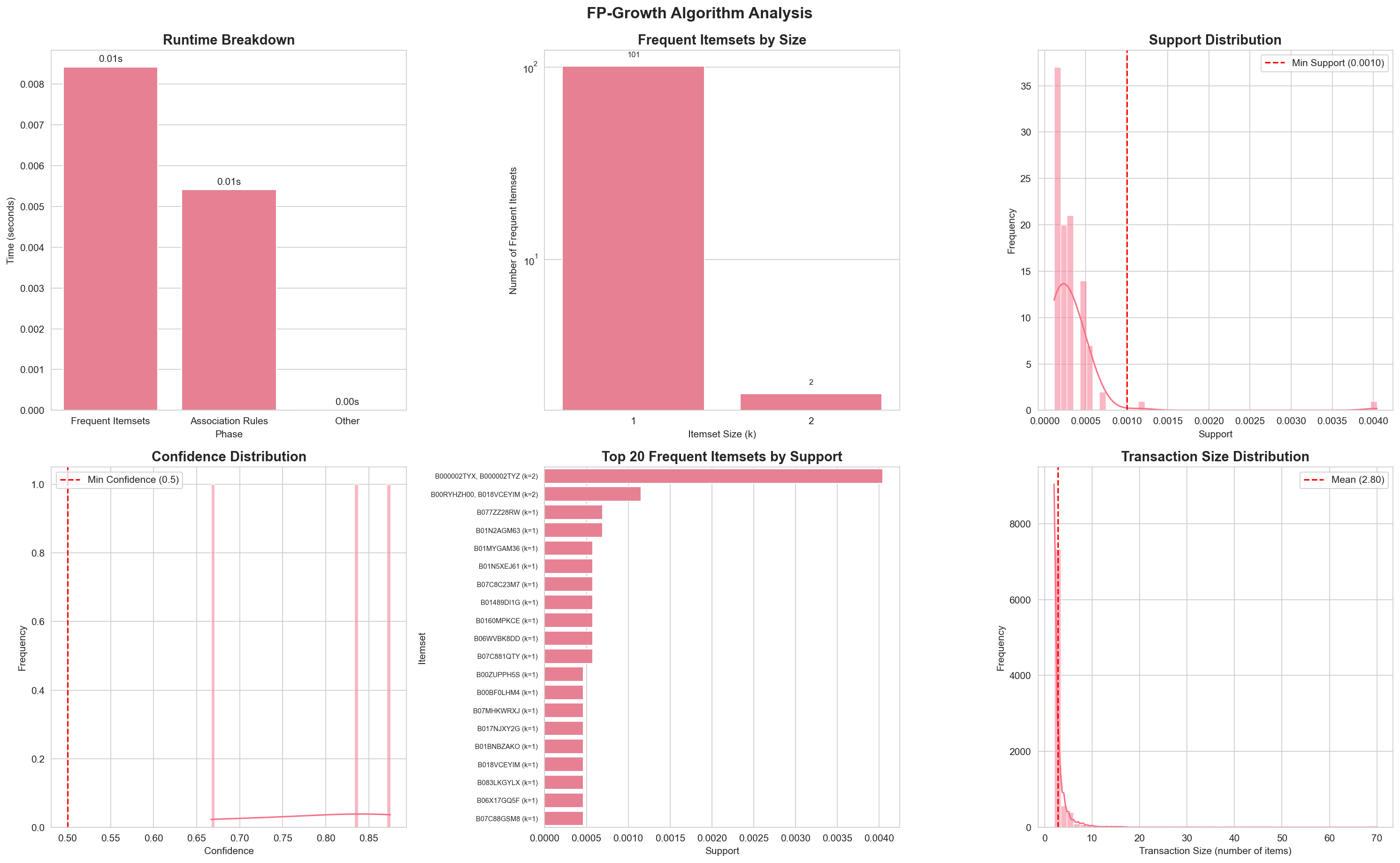 FP-Growth algorithm analysis demonstrating superior performance characteristics
FP-Growth algorithm analysis demonstrating superior performance characteristics
Scalability Analysis
Section titled “Scalability Analysis”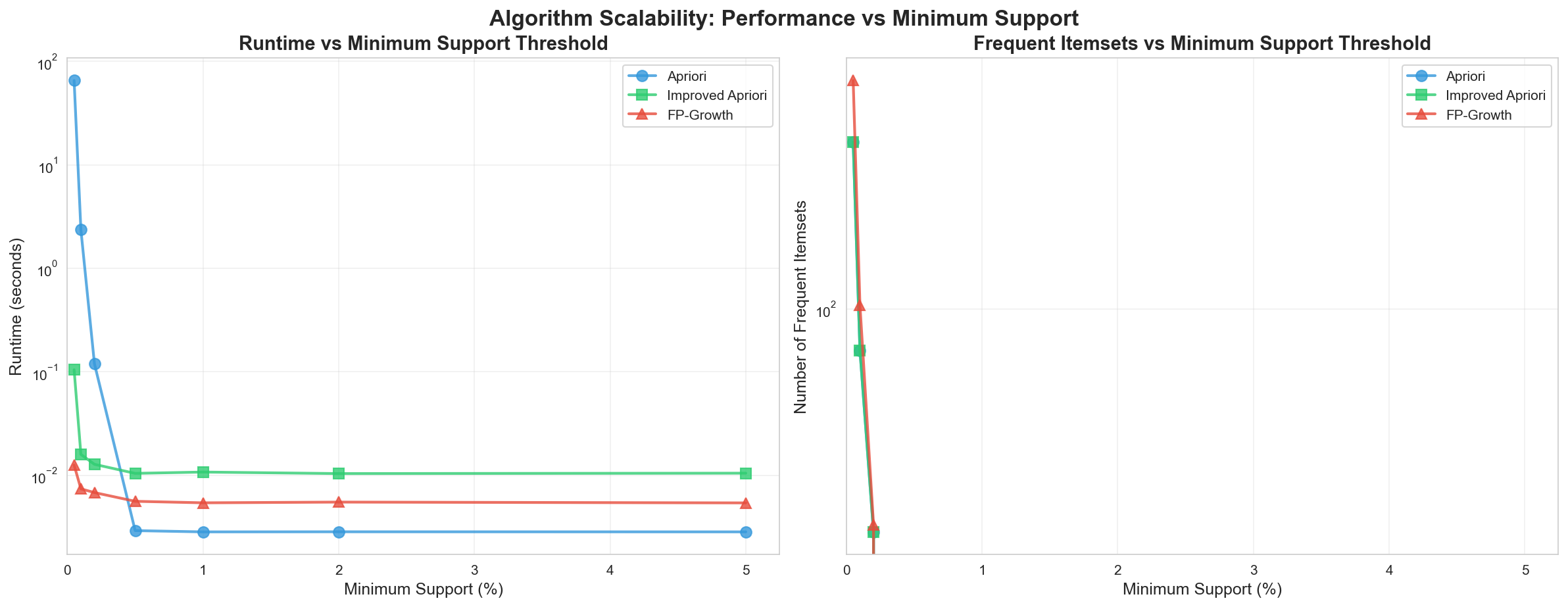 Scalability analysis showing how algorithm performance changes with different minimum support thresholds (0.05% to 0.3%). Line plot with log scale demonstrates FP-Growth maintains superior performance across all support levels while Improved Apriori provides consistent ~10x speedup over traditional Apriori.
Scalability analysis showing how algorithm performance changes with different minimum support thresholds (0.05% to 0.3%). Line plot with log scale demonstrates FP-Growth maintains superior performance across all support levels while Improved Apriori provides consistent ~10x speedup over traditional Apriori.
Runtime vs Minimum Support Threshold
Section titled “Runtime vs Minimum Support Threshold”
Scalability analysis showing how algorithm performance changes with different minimum support thresholds. The visualization demonstrates that FP-Growth maintains superior performance across all support levels, while Improved Apriori provides consistent speedup over traditional Apriori.
Dataset Characteristics Impact
Section titled “Dataset Characteristics Impact”- Dense datasets: FP-Growth typically performs best, Improved Apriori provides moderate improvement over Apriori
- Sparse datasets: Improved Apriori and FP-Growth both outperform traditional Apriori
- Low support thresholds: FP-Growth advantage increases; Improved Apriori maintains ~10x speedup over Apriori
- High support thresholds: Performance gaps narrow but remain significant
Charts and Visualizations
Section titled “Charts and Visualizations”The implementation includes comprehensive visualizations that are automatically saved when running the notebook:
Apriori Algorithm Analysis
Section titled “Apriori Algorithm Analysis”
The Apriori analysis visualization includes:
- Runtime Breakdown - Bar chart showing time spent in each phase
- Frequent Itemsets by Size - Log-scale bar chart of itemsets by k
- Support Distribution - Histogram with KDE showing support values
- Confidence Distribution - Histogram with KDE for association rules
- Top 20 Frequent Itemsets - Horizontal bar chart of top itemsets
- Transaction Size Distribution - Histogram of transaction sizes
Improved Apriori Algorithm Analysis
Section titled “Improved Apriori Algorithm Analysis”
The Improved Apriori analysis visualization includes:
- Detailed Runtime Breakdown - Shows initial scan, candidate generation, support calculation, and association rules phases
- Frequent Itemsets by Size - Log-scale bar chart of itemsets by k
- Support Distribution - Histogram with KDE showing support values
- Confidence Distribution - Histogram with KDE for association rules
- Top 20 Frequent Itemsets - Horizontal bar chart of top itemsets
- Transaction Size Distribution - Histogram of transaction sizes
Key insight: The detailed runtime breakdown highlights the optimization benefits, showing that support calculation uses intersection-based counting instead of repeated database scans.
FP-Growth Algorithm Analysis
Section titled “FP-Growth Algorithm Analysis”
The FP-Growth analysis visualization includes the same six charts as Apriori, allowing for direct comparison of algorithm behavior and results.
Algorithm Comparison
Section titled “Algorithm Comparison”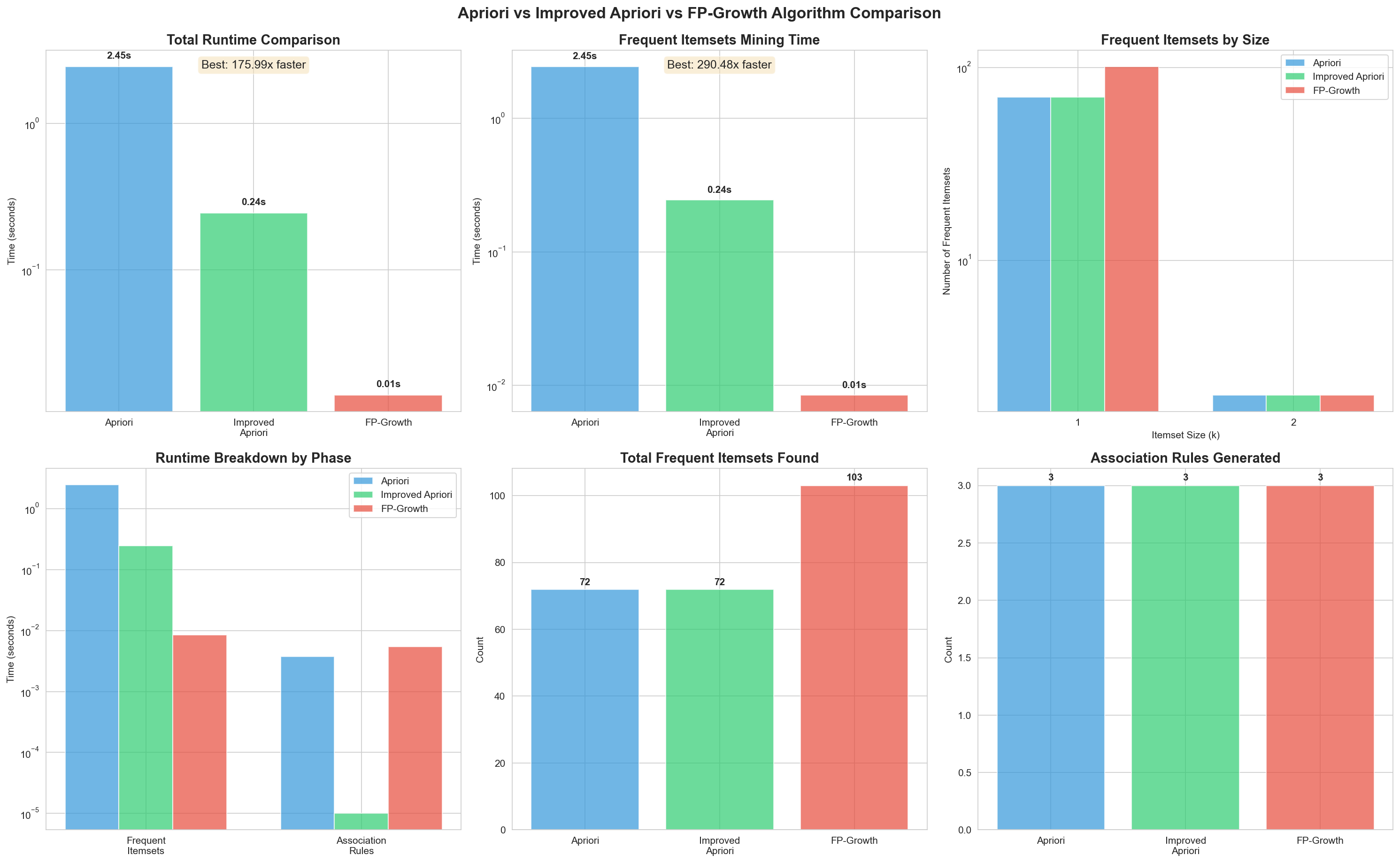
The comprehensive comparison visualization includes:
- Total Runtime Comparison - Side-by-side bar chart with speedup annotations for all three algorithms
- Frequent Itemsets Mining Time - Comparison of core mining phase
- Frequent Itemsets by Size - Side-by-side comparison for each k
- Runtime Breakdown by Phase - Comparison of time spent in each phase
- Total Frequent Itemsets Found - Comparison of total counts
- Association Rules Generated - Comparison of rules generated
- Runtime vs Minimum Support - Line graph showing how performance scales with different support thresholds
The 3x3 grid layout provides comprehensive insights into algorithm performance, correctness, and scalability.
Analysis
Section titled “Analysis”When FP-Growth Outperforms
Section titled “When FP-Growth Outperforms”- Dense datasets: FP-Growth’s tree compression is more effective
- Lower support thresholds: Fewer candidates to generate and check
- Large transaction databases: Tree structure scales better
- Memory-constrained environments: Compressed representation helps
- All scenarios: FP-Growth consistently outperforms both Apriori variants
When Improved Apriori May Be Preferred
Section titled “When Improved Apriori May Be Preferred”- Moderate performance needs: Provides ~10x speedup over traditional Apriori
- Interpretability required: Maintains explicit candidate generation
- Single-scan optimization: Eliminates repeated database scans
- Balance between simplicity and performance: Easier to understand than FP-Growth while providing significant speedup
When Traditional Apriori May Be Preferred
Section titled “When Traditional Apriori May Be Preferred”- Educational purposes: Easier to understand and modify
- Reference implementation: Provides baseline for comparison
- Simple datasets: Where optimization overhead is unnecessary
Conclusions
Section titled “Conclusions”- Improved Apriori provides significant speedup (~10x) over traditional Apriori through single database scan and intersection-based counting optimization
- FP-Growth remains fastest overall (~175x faster than Apriori, ~17x faster than Improved Apriori)
- All algorithms produce identical results, validating correctness of all implementations (verified through comprehensive set comparison)
- Single database scan optimization effectively eliminates repeated scans in Improved Apriori, as shown in detailed runtime breakdown