FP-Growth Algorithm
FP-Growth Algorithm Overview
Section titled “FP-Growth Algorithm Overview”The FP-Growth (Frequent Pattern Growth) algorithm is an efficient alternative to the Apriori algorithm for mining frequent itemsets. It was proposed by Han et al. in 2000 and uses a tree-based data structure to compress the database representation.
Algorithm Steps
Section titled “Algorithm Steps”- Scan database: Count support for each item and identify frequent 1-itemsets
- Sort items: Order items by frequency (descending) and remove infrequent items
- Build FP-Tree: Construct the FP-tree by inserting transactions one by one
- Mine FP-Tree: Recursively mine the FP-tree to find all frequent itemsets
- For each item in the header table (from least frequent to most):
- Generate conditional pattern base
- Construct conditional FP-tree
- Recursively mine the conditional FP-tree
- For each item in the header table (from least frequent to most):
FP-Tree Construction
Section titled “FP-Tree Construction”The FP-tree is built by:
- Sorting items in each transaction by frequency
- Inserting transactions as paths in the tree
- Sharing common prefixes between transactions
- Maintaining header tables for efficient traversal
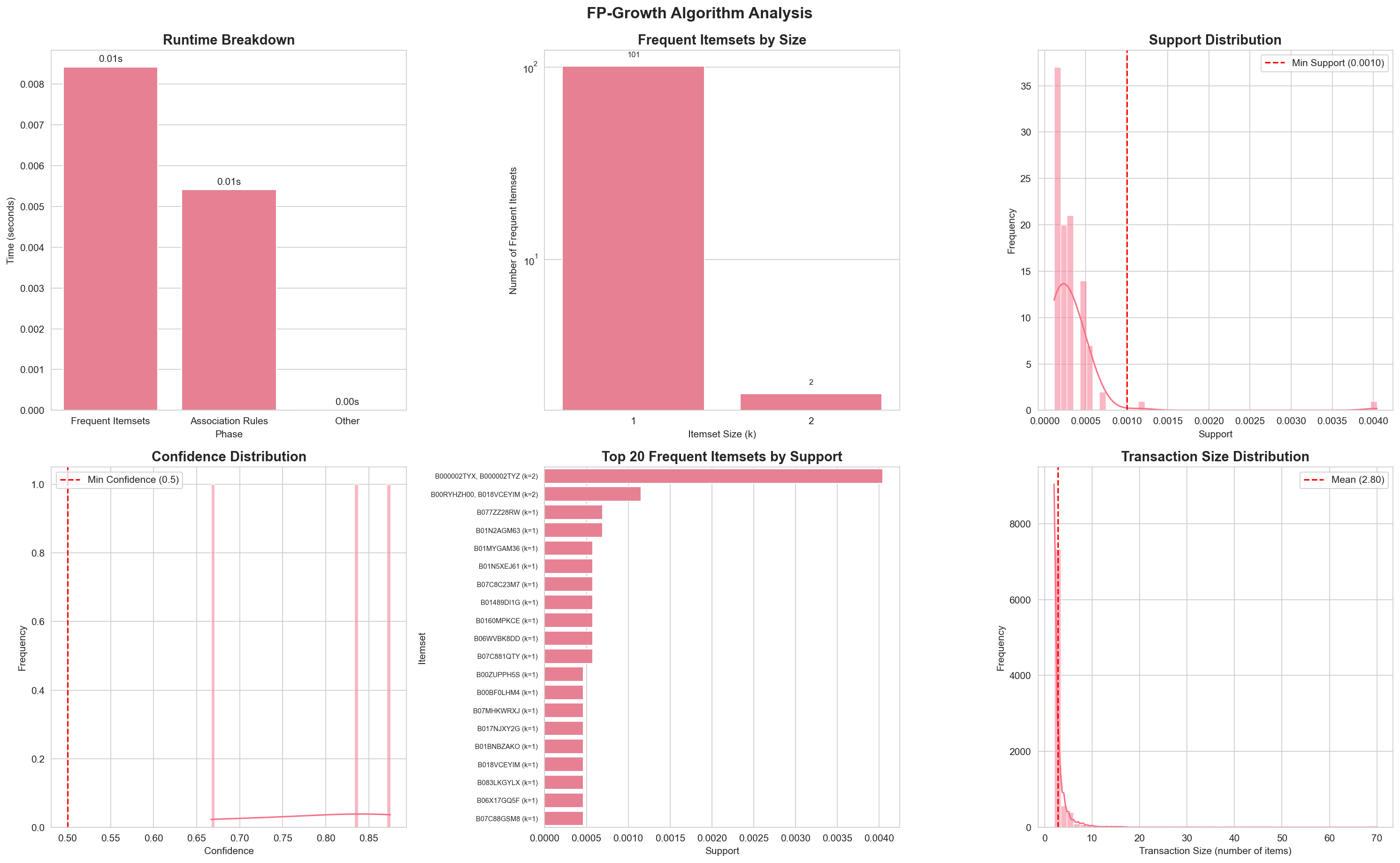
Experimental Results
Section titled “Experimental Results”Our implementation demonstrates FP-Growth’s superior performance compared to Apriori. See the Results page for detailed performance analysis and comparison.
Relationship to Improved Apriori
Section titled “Relationship to Improved Apriori”While FP-Growth offers a fundamentally different approach, understanding both algorithms helps in:
- Comparing performance characteristics
- Understanding trade-offs between approaches
- Developing hybrid methods
- Applying concepts from FP-Growth to improve Apriori-based algorithms